Technique behind git
tags:
git
author:
Chungyi Chi
-
參考資料
- Git 原理入門 介紹的非常好,可以直接看這篇也無所謂
- Write yourself a Git! 有介紹如何產生 hash value,以及實作了一個並不完整的 git
- Git Tip of the Week: Objects and Packfiles
git 是一個非常簡單暴力的東西,git 就是一棵樹,跟一堆指標的集合體,與其說他是版本控制的軟體,他像是一個簡易的「檔案系統」,你使用的所有檔案,都是從 .git 資料夾中的資訊還原出來的
首先我們初始化一個專案,會看到 .git 資料夾下有如下資料夾,但如果是要了解 git 如何運作,我們只需要關注 objects 跟 refs 這兩個資料夾即可 * objects: 儲存 git objects * refs: 儲存 remote / local branch 的資訊
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:40 暮]~/testgit> git init
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/demonic/testgit/.git/
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:40 暮]~/testgit> ls .git/
branches config description HEAD hooks info objects refs
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:40 暮]~/testgit> ls .git/objects/
info packgit objects
在 git 的術語中,我們會有四種不同的 git objects 他們的資料結構及意義都稍有不同
- Blob: 對應到一個檔案,所有的檔案資料,都會被存成這個格式
- Tree: 對應到一個資料夾,並指向資料夾底下的資料,也就是指向 Blob
- Commit(branch): 存放 Commit 資訊,且指向一顆 Tree,而第一顆 Tree 指的就是我們作業的 root 資料夾
- Tags: 一個固定不動的指標,常用來做 release 的 commit 定位
而我們的檔案系統,就是由以上四種 object 為基礎,會去組成一顆 working tree,如下圖一般
(下圖引用自
Git 原理入門
)
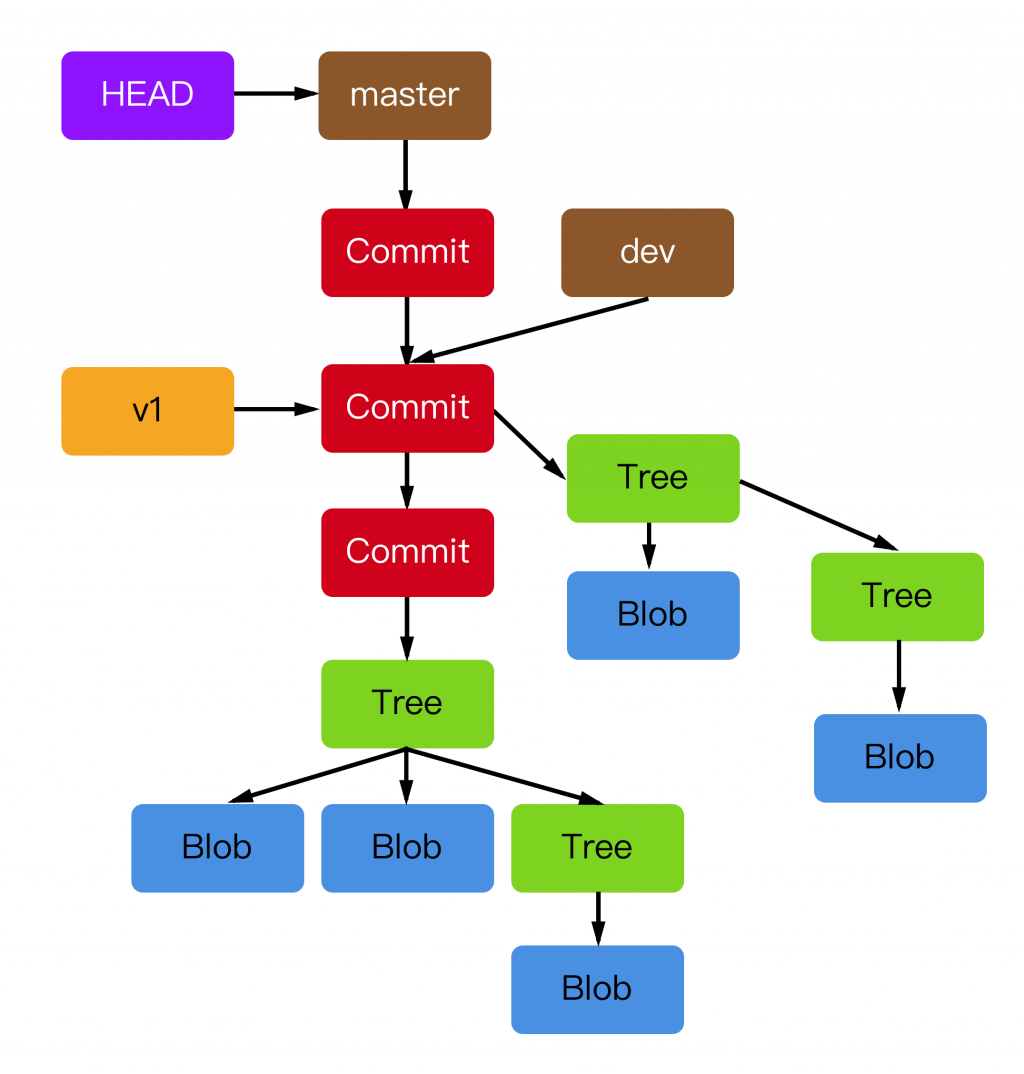
讓我們繼續操作我們剛剛所新增的專案,來理解這顆樹到底是什麼玩意
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:40 暮]~/testgit> ls .git/objects/
info pack
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:40 暮]~/testgit> echo "Hello" > string.txt
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:47 暮]~/testgit> cat string.txt
Hello
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:47 暮]~/testgit> ls .git/objects/
info pack
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:47 暮]~/testgit> git add string.txt
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:47 暮]~/testgit> ls .git/objects/
e9 info pack
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:47 暮]~/testgit> ls .git/objects/e9/
65047ad7c57865823c7d992b1d046ea66edf78我們新增了一個檔案,但這個時候還沒有作 commit,只是把他 add 進來,就發現 objects 的資料夾已經多了一個資料夾,且儲存了一串 hash 值,這資料夾的名稱及 hash 值,其實就是拿這個檔案的內容去作 SHA 而得的,這會取前兩個字元作為資料夾名稱,我們並沒有要實作一個 git,這部份的演算法不用太過琢磨
但光這樣說恐怕還是不太明白,讓我們使用 git cat-file 來看看這個檔案裡到底儲存了什麼,會發現只是一個單純的 Hello 字串,而這就是一個典型的 blob 的 git object
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:49 暮]~/testgit> git cat-file -p e965
Hello而當我們把他加到 commit 中之後,會發現 objects 中又多了兩個資料夾,我們可以根據他們的 hash 值一個一個拿出來看,最後會知道這就是 tree 以及 commit git object
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:51 暮]~/testgit> git commit -m "add hello"
[master (root-commit) 38d6d56] add hello
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 string.txt
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:51 暮]~/testgit (master)> ls .git/objects/
38 ab e9 info pack
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:51 暮]~/testgit (master)> git cat-file -p e965
Hello
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:51 暮]~/testgit (master)> git log --oneline
38d6d56 (HEAD -> master) add hello
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:52 暮]~/testgit (master)> git cat-file -p 38d6
tree abc0fa8606702a03eec14cda420c40288a65f8a6
author demonic <ian910297@gmail.com> 1589550697 +0800
committer demonic <ian910297@gmail.com> 1589550697 +0800
add hello
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:52 暮]~/testgit (master)> git cat-file -p abc0
100644 blob e965047ad7c57865823c7d992b1d046ea66edf78 string.txt
如果把上述的操作對應到原本那張 working tree,他們所在的位置就會長這樣,只是我沒有開那麼多個資料夾以及檔案,也沒下那麼多 commit,所以現在只能表示到第一個 commit 的位置

我們接下來嘗試對原本的 git object 作修改,再次 commit,卻發現他並不是針對原本的 blob 檔案作修改,而是又新增了一個全新的 blob 檔案,來儲存字串的資訊
demonic@demonic-All-Series[09:55 暮]~/testgit (master)> echo ", World" >> string.txt
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:04 暮]~/testgit (master)> cat string.txt
Hello
, World
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:04 暮]~/testgit (master)> git add .
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:04 暮]~/testgit (master)> git commit -m "add world"
[master 8398b1e] add world
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:04 暮]~/testgit (master)> git cat-file -p 8398
tree f1884295ba39a447d2de1adfa02bf5421838005f
parent 38d6d5613f892d8771c231648c689191e9f9baeb
author demonic <ian910297@gmail.com> 1589551488 +0800
committer demonic <ian910297@gmail.com> 1589551488 +0800
add world
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:05 暮]~/testgit (master)> git cat-file -p f188
100644 blob c797a227050cf7befb554b432e2301d1b1df2145 string.txt
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:05 暮]~/testgit (master)> git cat-file -p c797
Hello
, World
對應到圖會長這樣

這樣的機制會導致一個問題,會有大量的小型 blob 檔案出現,所以 git 有一個 gc 指令,會把 git objects 壓縮成兩個檔案,分別是 .idx 以及 .pack,.idx: 用作查找 .pack 檔案的索引,會記錄每個 object 在 .pack 中的長度以及 offset,如下指令就把 objects 壓縮了
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:05 暮]~/testgit (master)> ls .git/objects/
38 83 ab c7 e9 f1 info pack
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:11 暮]~/testgit (master)> git gc
Counting objects: 6, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (6/6), done.
Total 6 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:11 暮]~/testgit (master)> ls .git/objects/
info pack
demonic@demonic-All-Series[10:11 暮]~/testgit (master)> ls .git/objects/pack/
pack-ade866cad626ae442179508a693b12a9a5ee5d97.idx
pack-ade866cad626ae442179508a693b12a9a5ee5d97.pack壓縮後並不影響我們查找,因為會去找 .idx 來要資訊~~
最後我們終於可以介紹 Branch 跟 Tag 是什麼玩意了,這兩個東西都是一個指向 Commit object 的指標,但 tag 不會動,branch 會一直往下走,這相關的資訊儲存在 refs 資料夾,可以自行去 cat 其中檔案資訊出來看,會儲存對應的 commit hash value
總之,從以上資訊,我們應該已經對 git 如何作版本控管有一定了解
-
問題討論
-
git add 是如何作檔案差異比較 我們推測是由 string diff 的程式著手,一行一行進行比較,而不是針對整棵 working tree 去作比較,因為比較兩顆樹的演算法,通常都過於複雜,但比較字串,他算是被簡化成一個 LCS(Longest Common Sequence) 問題
-
git 是區塊鏈嗎 git 雖然是由不同的 hash 值一個串一個而成,雖然不好偽造,但如一開始所說,他比較像是一個檔案系統,你偽造他有啥意義嗎@@ 而且這也沒有 PoW 相關機制
不過真的有人把 git porting 到區塊鏈上,變成一種應用,如: Mango: Git completely decentralised ,這是把資料存到 IPFS 上,這樣就不需要額外架設一個 git server 了